Corrugated plastic sheets are versatile, durable, and lightweight materials widely used in signage, packaging, construction, and DIY projects. However, to maximize their potential, knowing the best way to cut corrugated plastic sheets is essential. Proper cutting techniques ensure clean edges, reduce waste, and save time.
In this article, we will explore different cutting methods, tools, tips, and safety considerations to help you work efficiently with corrugated plastic. Whether you’re a professional or a hobbyist, understanding the best way to cut corrugated plastic sheets will improve your project outcomes.

Before diving into cutting methods, it’s important to understand why the cutting technique affects your results. Corrugated plastic sheets consist of twin-wall polypropylene, featuring fluted channels that provide strength and flexibility.
Choosing the best cutting method means balancing precision, speed, and safety. For instance, cutting too quickly or with the wrong tool can damage the sheet, making it unusable and increasing costs. Similarly, improper technique can affect how sheets fit together in applications such as signage or construction panels.
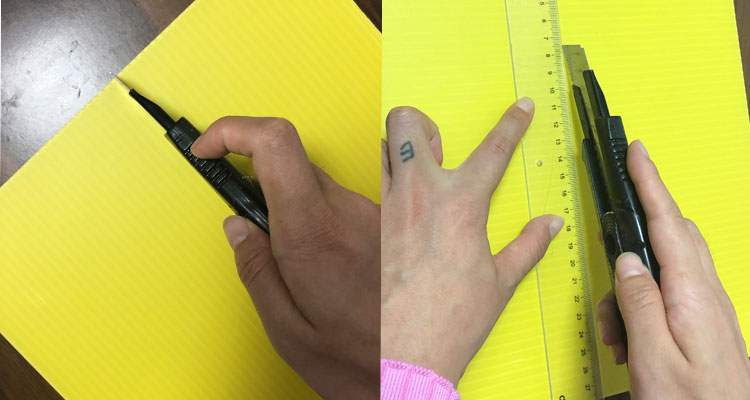
The utility knife is one of the most common tools for cutting corrugated plastic sheets, especially for thinner sheets (usually under 6mm thickness).
Expanded Explanation:
The utility knife remains the go-to tool for many users because it offers excellent control and precision at a low cost. However, scoring takes patience — you must press firmly and score multiple passes along the same line to achieve a clean break. Thicker sheets may require additional effort or alternative cutting methods.
Table 1: Utility Knife Suitability
| Sheet Thickness (mm) | Recommended Use | Blade Replacement Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 – 4 | Ideal for straight cuts | After every 10 cuts |
| 5 – 6 | Possible but requires multiple passes | After every 5-7 cuts |
| Above 6 | Not recommended | N/A |
For thicker or larger sheets, a circular saw with a fine-tooth blade designed for plastics can be used.
Expanded Explanation:
Using a circular saw improves efficiency when working with multiple sheets or thick materials (above 6mm). It’s critical to choose a blade with fine teeth to avoid chipping the plastic. A slower cutting speed reduces melting from friction heat, preventing rough edges. Clamp the sheet securely to prevent vibrations that can ruin the cut.
Table 2: Circular Saw Blade Types
| Blade Type | Teeth Count | Best For | Cutting Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-tooth Carbide | 80 – 120 | Plastics & composites | Slow to moderate |
| Standard Wood Blade | 40 – 60 | Wood, not recommended for plastic | Moderate to fast |
| Diamond-tipped | 100+ | Extremely hard plastics | Slow |
A jigsaw is useful for curved or irregular cuts.
Expanded Explanation:
A jigsaw is ideal when you need to make non-linear cuts that a circular saw or utility knife cannot achieve. When using a jigsaw, select blades specifically designed for plastics, often labeled as “fine tooth” or “high TPI (teeth per inch).” Moving the saw slowly reduces friction heat, preventing the edges from melting or becoming ragged. Additionally, securing the sheet firmly with clamps prevents movement and enhances precision.
Table saws offer the most precision for high-volume cutting.
Expanded Explanation:
For industrial or workshop environments, a table saw can deliver repeatable cuts with high accuracy. Using the right blade, typically carbide-tipped with many teeth, ensures smooth edges. Operators should always use push sticks and guards to protect hands. This method suits large-scale production but requires upfront investment and proper training.
A hot knife melts through the plastic, creating smooth edges.
Expanded Explanation:
The hot knife cutter uses a heated blade to slice through corrugated plastic sheets by melting the material along the cut line. This prevents jagged edges or cracks, offering a smooth finish, particularly for complex shapes. However, this tool is less common for casual use due to equipment cost and power requirements. Also, care must be taken to avoid fumes from melting plastic.
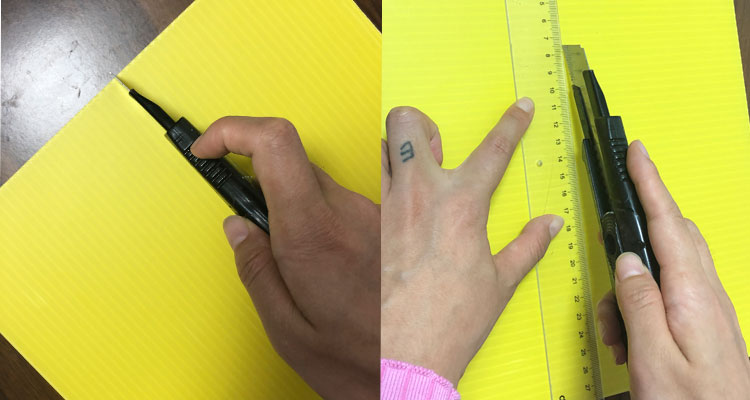

Expanded Explanation:
Before cutting, ensure your work surface is clean and flat to prevent unwanted damage. Use a metal ruler or straightedge to guide your knife for perfectly straight cuts. Keep your hand steady, and avoid rushing the scoring steps; the more passes you make with the blade, the cleaner the final break will be. After snapping the sheet, inspect edges and lightly sand to remove any burrs or roughness, enhancing safety and appearance. Always wear protective gloves to avoid injury during cutting and sanding.
Expanded Explanation:
Proper preparation before cutting greatly influences results. Clamping or weighting the sheet prevents movement, which can cause inaccurate or jagged cuts. Wearing gloves protects your hands from accidental nicks, and eyewear guards against flying debris. Temperature can also affect cutting—warmer conditions soften plastic, increasing the risk of melting if you cut too quickly. Patience and safety first will improve your cutting efficiency.
Expanded Explanation:
Rushing to finish a cut can damage the plastic and increase wastage. Blunt blades require more pressure, often resulting in uneven cuts and dangerous slips. Securing the sheet is critical; even slight movements can ruin the alignment. Always respect safety protocols, especially when using power tools, to prevent accidents and protect your health.
Mastering the best way to cut corrugated plastic sheets depends on selecting the right tools and techniques suited to your sheet thickness and project requirements. From simple utility knives for DIY projects to power saws for industrial tasks, following best practices will yield clean, precise results every time.
If you are looking for high-quality corrugated plastic sheets, Polyflute offers a wide range of durable, customizable options. Contact us today to find the perfect sheets for your next project!