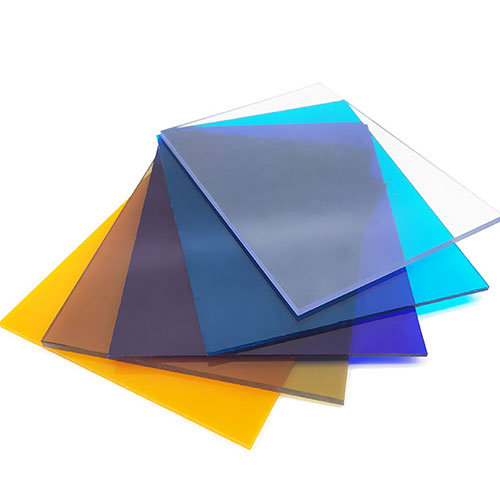
Polycarbonate sheets and plexiglass (acrylic) are popular transparent plastics used in construction, signage, DIY projects, and industrial applications. Both are lightweight, durable, and versatile alternatives to glass, but they differ in performance, cost, sustainability, and ease of fabrication. The choice between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass depends on specific needs—such as impact resistance and UV protection for a greenhouse or optical clarity and fabrication ease for retail displays. This article explores the differences between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass in terms of composition, mechanical properties, applications, cost, workability, and environmental impact, providing a comprehensive guide to help you choose the best material for your project.

When discussing polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass, it’s essential to begin by understanding the fundamental differences in their chemical composition and how these affect their physical properties. Although both are thermoplastics and often used as substitutes for glass, the way they are formulated and behave under various conditions is markedly different.
Polycarbonate is a synthetic resin in the polyester family of polymers. It is made from bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene. The result is a material with a high molecular weight and an intrinsic toughness that stands out even among high-performance plastics. The unique structure of polycarbonate allows it to:
Polycarbonate is also about 200 times more impact-resistant than glass and significantly more durable than plexiglass, making it the go-to material for security glazing, riot shields, and bullet-resistant windows.

Plexiglass, or polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is an acrylic polymer that is manufactured through a process of polymerizing methyl methacrylate. It has a linear structure that gives it impressive light transmission and weather resistance, though it is more brittle than polycarbonate. Key features of plexiglass include:
Due to these properties, plexiglass is often used for applications where clarity and aesthetic appearance are crucial, such as picture frames, signage, aquariums, and display cases.
| Property | Polycarbonate Sheets | Plexiglass (Acrylic Sheets) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Extremely high | Moderate |
| Light Transmission | ~88% | ~92% |
| UV Resistance | Moderate (with coating) | High (inherent) |
| Temperature Tolerance | Up to 135°C | Up to 80°C |
| Scratch Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Weight | Light | Slightly lighter than PC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Moderate to high |
| Fire Resistance | Self-extinguishing (UL94 V-0) | Flammable unless modified |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
This table illustrates that when considering polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass, the former tends to outperform the latter in terms of impact resistance, thermal stability, and flexibility. However, plexiglass may be preferable in cases where higher clarity, scratch resistance, and aesthetic value are prioritized.
Polycarbonate excels in harsh environments. It is highly resilient against high-impact forces, making it suitable for industrial environments or areas prone to vandalism or accidents. Plexiglass, although rigid and beautifully transparent, can shatter or crack under heavy loads or sudden impact. This difference is crucial when selecting a material for safety applications like machine guards or bus shelters.
Moreover, polycarbonate can withstand drastic temperature changes, whereas plexiglass may become brittle in cold weather and warp when exposed to prolonged heat.
When the visual appearance is paramount, plexiglass is the clear winner. Its superior transparency makes it ideal for decorative elements, museum displays, and any application where light clarity must be maximized. On the other hand, polycarbonate’s slightly lower light transmission is usually unnoticeable to the naked eye but may matter in high-precision optical setups.
When it comes to choosing between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass, understanding the practical applications in various industries can be a game changer. Each material has unique characteristics that make it better suited for certain environments and uses. Let’s explore the specific applications where polycarbonate and plexiglass shine.
Polycarbonate is often the preferred choice in environments where durability, impact resistance, and safety are paramount. Some key industries that benefit from polycarbonate sheets include:
Polycarbonate sheets are frequently used in the construction of skylights, roofing systems, and wall cladding, particularly in areas where safety and insulation are top priorities. Their high impact resistance makes them ideal for protecting buildings from natural disasters, vandalism, and accidents.
In addition, polycarbonate is used for energy-efficient windows and roof panels due to its thermal insulation properties. Greenhouses, for example, often use multi-wall polycarbonate sheets because of their excellent heat retention and UV resistance.
Polycarbonate’s high impact resistance and optical clarity make it a popular material for automotive parts, including headlamps, windows, and sunroofs. It is also used for aircraft windows, cockpit shields, and interior panels in aerospace applications.
Polycarbonate’s strength allows for thinner, lighter panels compared to glass, leading to weight savings in the automotive and aerospace industries. This makes it an ideal material for improving fuel efficiency without compromising safety.
Polycarbonate’s unmatched impact resistance makes it the material of choice for applications where security is critical. Polycarbonate sheets are used in:
These applications benefit from polycarbonate’s ability to absorb and dissipate energy without breaking, providing an essential level of safety in high-risk environments.
While polycarbonate is the go-to material for durability and impact resistance, plexiglass excels in areas where optical clarity, ease of processing, and aesthetic appeal are the primary concerns. Key industries where plexiglass is commonly used include:
Plexiglass is frequently used in the production of illuminated signs, display cases, and storefront windows. Its ability to be easily fabricated into intricate shapes and its excellent light transmission make it a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor signage.
The material’s transparency and ease of machining make it perfect for applications where visual appeal is paramount.
For aquariums, fish tanks, and other water features, plexiglass is the preferred material due to its ability to be shaped into large, smooth panels that provide clear visibility. Unlike glass, plexiglass is less likely to shatter under pressure or stress, making it safer for both the fish and people handling the tanks.
Plexiglass is also used for display tanks in museums and exhibitions, where clarity and the ability to shape the material into custom designs are crucial.
Plexiglass is often used in the automotive and marine industries, particularly for non-structural applications where optical clarity is needed. For instance:
In both these industries, while plexiglass is not as impact-resistant as polycarbonate, it provides the perfect balance between clarity, lightweight properties, and ease of fabrication.
Plexiglass is used for creating stunning light fixtures, partitions, and decorative panels in interior design. Its clarity, coupled with the ability to add vibrant color and light effects, makes it a favorite for designers looking to create modern, aesthetic interiors.
Both polycarbonate and plexiglass serve distinct roles in different industries. Polycarbonate excels in environments where safety, impact resistance, and strength are essential, such as in construction, security, and automotive applications. On the other hand, plexiglass shines in scenarios where aesthetic clarity, ease of processing, and lightweight properties are prioritized, such as in signage, displays, and interior design.
The key takeaway when considering polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass is that each material’s suitability depends heavily on the specific needs of the application. While polycarbonate is the more durable and secure option for heavy-duty uses, plexiglass offers superior clarity and aesthetic versatility for design-focused projects.

When deciding between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass, cost is always a significant factor, particularly when considering large-scale projects or long-term investments. While the initial price difference might seem obvious, the total cost of ownership—including maintenance, durability, and longevity—must also be considered. Let’s examine how the upfront costs compare and how long-term value factors into the decision-making process.
At first glance, plexiglass is typically less expensive than polycarbonate. This price disparity makes plexiglass an attractive choice for projects where budget constraints are a concern, especially for non-structural uses or decorative applications. Plexiglass can often be purchased at a fraction of the cost of polycarbonate sheets, especially for smaller quantities or less demanding applications.
However, it’s essential to note that while plexiglass is cheaper initially, its lower impact resistance means it might need to be replaced more frequently in high-risk or high-traffic applications. This could increase long-term costs over time, especially if the material suffers damage that requires replacement.
While polycarbonate sheets have a higher upfront cost, their durability often provides greater long-term value. Polycarbonate is much more resistant to impact and wear, and its toughness ensures that it will stand up to the rigors of harsh environments for years. For applications like security windows, roofing, or machine guards, the longevity and safety provided by polycarbonate justify the higher price.

When deciding between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass, the total cost of ownership should guide your decision. Although plexiglass is cheaper upfront, polycarbonate may be the more cost-effective option for applications requiring high strength, durability, and long-term performance. For applications where durability is not as crucial, such as in decorative or indoor environments, plexiglass’s lower cost may make it the better choice.
Here are some examples of how each material fits into different project types:
the choice between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass often comes down to the specific requirements of the project and the long-term value each material offers. While plexiglass is more affordable and provides excellent clarity, polycarbonate’s higher initial cost is balanced by its superior durability, impact resistance, and long-lasting performance in demanding environments.
For those on a budget, plexiglass may seem like the right option, but when factoring in potential replacements and the need for extra maintenance, polycarbonate can often be the more economical choice over time.

The choice between polycarbonate sheets vs plexiglass should be guided by the specific needs of the project. If the primary concern is safety, impact resistance, and longevity, polycarbonate is likely the better choice. Its ability to withstand harsh environments and physical stress makes it ideal for outdoor, security, and industrial applications.
However, for projects that prioritize cost savings, optical clarity, and decorative value, plexiglass may be the more suitable option. It’s perfect for lighter-duty applications where impact resistance is not a major concern, such as in interior displays, picture frames, and signage.
Ultimately, both polycarbonate and plexiglass have their place in modern construction, manufacturing, and design. While polycarbonate’s superior durability and toughness make it the go-to choice for high-stakes applications, plexiglass remains a strong contender for its clarity, ease of use, and affordability. By carefully considering the factors of cost, performance, durability, and environmental impact, you can make an informed decision that best meets the needs of your project.
Whether you’re choosing polycarbonate sheets or plexiglass, the key is to match the material to the specific demands of the application. Both materials are versatile, durable, and have their own strengths and weaknesses. Therefore, it’s important to weigh these factors carefully before making your final selection. Welcome to contact Poluflute to get more information about the polycarbonate sheets.